Pattern Toolings
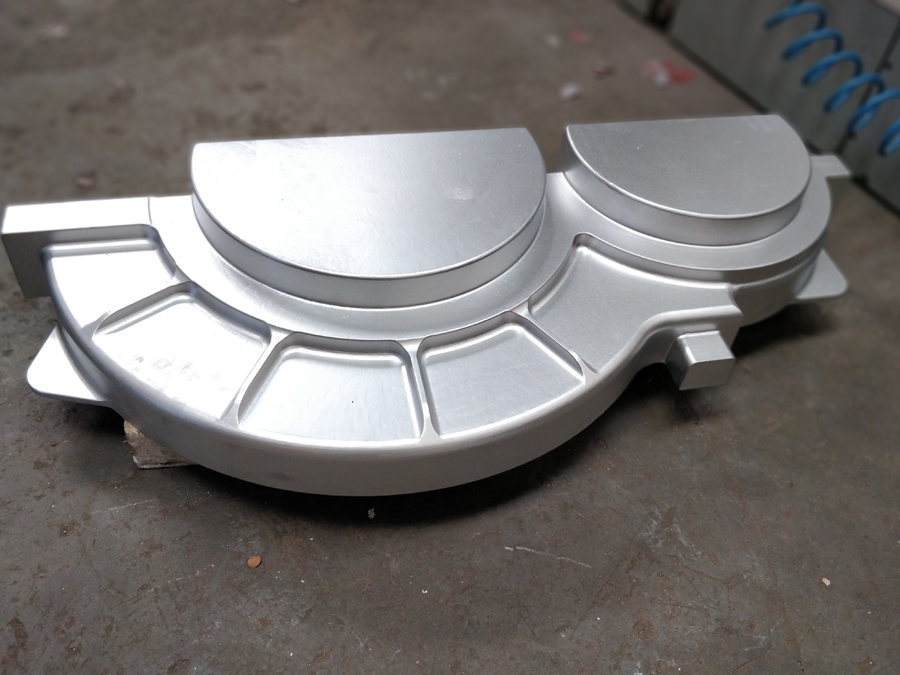
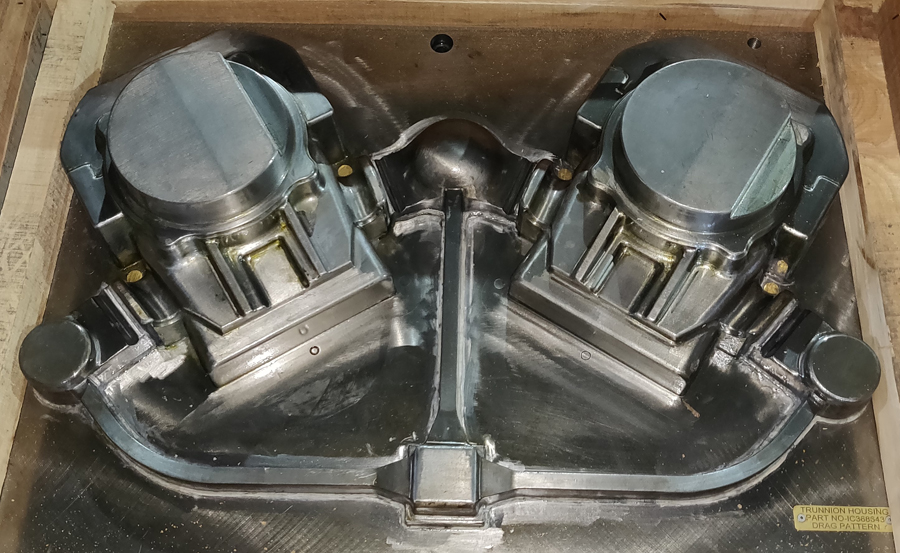
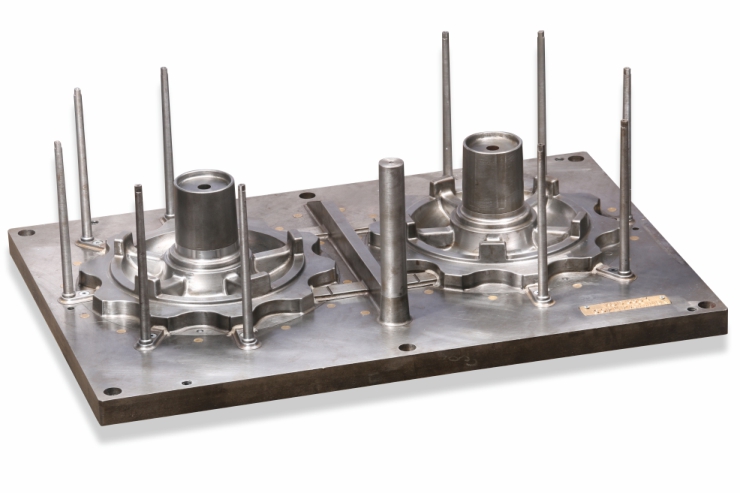
Patterns are used to create the shape in the sand, into which molten metal will be poured to become the casting. Patterns can be made from metal. Most patterns are made from aluminum, called match plates and have a long life before wearing out. Pattern Makers also manufacture the core boxes required (see under Core Making). Shell core boxes can be made in cast iron, steel or aluminum. CO2 core boxes are made in aluminum or Cast Iron.
We have highly experienced patternmakers to make any type of core box, or model that can be designed. We can make pattern by various grade Aluminum, Steel, Cast iron.
We undertake pattern/core box design and construction, gating and risers, alterations to existing tooling, and cast ability enhancements. Foundry tooling consists of patterns, core boxes, models and all the rigging that makes a complete job ready to run in a foundry.
Specializing in hand fabricated, and CNC machined patterns, our skilled craftsman can create loose patterns, match plates, cope and drag patterns and boxes, shell patterns, custom flexible patterns, and machine specific mounted patterns. Patterns are produced from aluminum, iron, and tool steels, and utilize the latest CAD/CAM systems to ensure precision.
No matter the process or material required, we can create the pattern that meets all of your needs and specification. We’ve worked with customers in a wide range of industries, and have gained a reputation of quality and craftsmanship.
Materials Used in Pattern Making:
Aluminium
- Properties: Aluminum alloys are lightweight, corrosion-resistant, and easily machinable. They offer good thermal conductivity, making them suitable for rapid prototyping and pattern making applications.
- Applications: Aluminum patterns are commonly used in foundries and manufacturing facilities for creating molds, cores, and prototypes for casting processes. They are ideal for low to medium volume production runs and applications where weight reduction is important.
Cast Iron
- Properties: Cast iron exhibits excellent compressive strength, making it suitable for applications where components undergo heavy loads or pressure. Cast iron has good resistance to wear and abrasion, making it ideal for components subjected to frictional forces.
- Applications: Engine blocks, cylinder heads, brake discs, and exhaust manifolds. Machine tool components, pump housings, valve bodies, and gears.
EN8 Steel
- Properties: EN8 steel is a medium carbon steel known for its good tensile strength, wear resistance, and machinability. It offers excellent weldability, making it suitable for fabricating patterns and tooling.
- Applications: EN8 steel patterns are used in sand casting, investment casting, and other casting processes to create molds, cores, and tooling for producing metal components. They are suitable for applications requiring durability, dimensional stability, and ease of machining.
H13 Steel
- Properties: H13 steel is a hot work tool steel characterized by its high hardness, excellent heat resistance, and good toughness. It exhibits superior wear resistance, making it ideal for demanding pattern making applications.
- Applications: H13 steel patterns are preferred for casting applications involving high temperatures and mechanical stresses. They are commonly used to produce molds, dies, and tooling for die casting, forging, and hot extrusion processes.
P20 Steel
- Properties: P20 steel is a low-alloy tool steel with good machinability, polishability, and toughness. It offers good wear resistance and dimensional stability, making it suitable for pattern making applications.
- Applications: P20 steel patterns are commonly used in plastic injection molding, die casting, and extrusion processes. They are suitable for creating molds, cores, and prototypes for plastic and metal components in low to medium volume production runs.
Pattern Making Process
- Patterns are designed based on engineering drawings, CAD models, or physical prototypes, specifying dimensions, features, and tolerances.
- The appropriate material (Aluminium, Cast iron, EN8 steel, H13 steel, or P20 steel) is selected based on factors such as strength, durability, machinability, and cost.
- Skilled patternmakers use cutting tools, shaping equipment, and CNC machining processes to fabricate the pattern from the chosen material.
- Multiple pattern pieces may be joined together using techniques such as welding or bolting to create complex patterns or assemblies.
- Patterns undergo surface treatment processes such as grinding, polishing, and coating to achieve the desired surface finish and dimensional accuracy.